Know everything about Fire Damp Explosion in Mines
Before dealing with Fire Damp..
Here we will discuss About the Definition of Explosion and also we will know about the types of Explosion in Mines...So Let's Go...
Q.What is Explosion?
Ans...:-
Here we will discuss About the Definition of Explosion and also we will know about the types of Explosion in Mines...So Let's Go...
Q.What is Explosion?
Ans...:-
Explosion can be defined as it the process of sudden change in the volume of any substance instantaneously into gaseous product which produces large quantity of heat energy.
Alike above explained, the explosion in mines are of three types.
In this post we will only discuss about "Fire Damp Explosion".
3. The explosibility limit is between 5.4 to 14.8 % of methane with rest to oxygen( limit is between 12.5% to 14.8%).
If the oxygen percentage is below 12 or equal 12, the mixture is not going to explode.
Alike above explained, the explosion in mines are of three types.
1. Firedamp Explosion
2. Coal Dust Explosion
3. Water Gas Explosion
In this post we will only discuss about "Fire Damp Explosion".
1. Explosion of Fire Damp(Methane)
Fire damp is the most common cause of explosion in Coal Mines. The Coal Dust Explosion alone is very rare though it have been initiated by fire damp many times.
The explosibility limit of firedamp is between 5.4 to 14.8% in presence of some ignition source and the percentage of Oxygen with respect to Methane percentage. "The maximum explosion is produced when the percentage of firedamp about 9".
The laboratory has proven that the sudden compression of gas-air mixture can be ignite when temperature and pressure raised simultaneously, gas-air mixture containing as low as 2% and as high as 75%.
The laboratory has proven that the sudden compression of gas-air mixture can be ignite when temperature and pressure raised simultaneously, gas-air mixture containing as low as 2% and as high as 75%.
The explosive mixture of Methane is once ignited, it will propagate independently away from the source.
Methane explosion has always two parts, the forward shock wave and the reverse wave.
Methane explosion has always two parts, the forward shock wave and the reverse wave.
Forward Shock Wave
When the gaseous products exploded, under high pressure a forwarding wave is created which travels away from the source of explosion of considerable force. This forward shock waves consumes all the oxygen.
Reverse wave
This result as the pressure drops at point of explosion as the gas cools and the product of explosion means water vapour condensate.
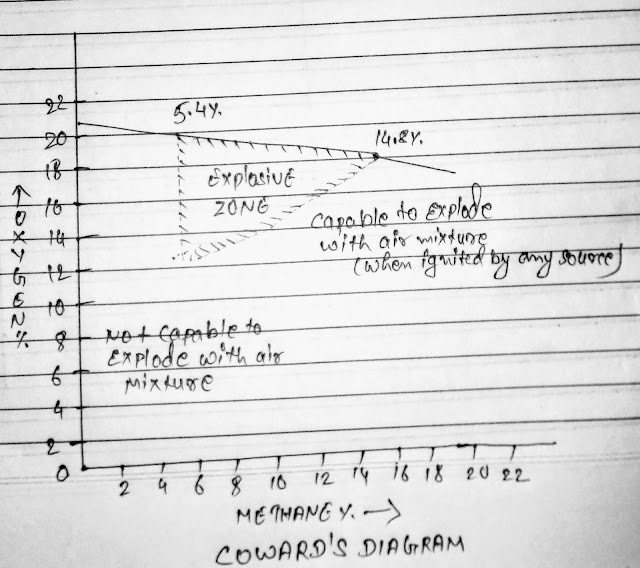
To understand properly the explosion in Mines we have Coward's Diagram...
So let's know...
Coward's Diagram
According to Coward's Diagram, the lowest explosibility limit of Meghan is 5.4 percent, when the sufficient heat or flame is applied.
Now we will discuss on Coward's graphic representation..
1. The mixtures which are in this triangular section is it self a explosive mixture.
2.As you can see in graph that the right side of graph contains too much methane but the mixture has not right amount if air to explode and the left side of this graph have not sufficient methane-air mixture to explode.
Now we will discuss on Coward's graphic representation..
1. The mixtures which are in this triangular section is it self a explosive mixture.
2.As you can see in graph that the right side of graph contains too much methane but the mixture has not right amount if air to explode and the left side of this graph have not sufficient methane-air mixture to explode.
3. The explosibility limit is between 5.4 to 14.8 % of methane with rest to oxygen( limit is between 12.5% to 14.8%).
If the oxygen percentage is below 12 or equal 12, the mixture is not going to explode.
A term ignition temperature is comes when we deal with methane explosion.
So, "the ignition temperature is the lowest temperature at which the explosion of methane starts". It is generally taken as 650℃ to 750℃.
The property of methane that it takes time to ignite. But it is considerable that when any combustible material is present with methane, the delay timing is affected. 30% of hydrogen is enough to eliminate the delay.
• The accumulation of Fire Damp should not exceed the lower limit.
So, "the ignition temperature is the lowest temperature at which the explosion of methane starts". It is generally taken as 650℃ to 750℃.
The property of methane that it takes time to ignite. But it is considerable that when any combustible material is present with methane, the delay timing is affected. 30% of hydrogen is enough to eliminate the delay.
Prevention of Explosion of Fire Damp
1.Prevent Dangerous Accumulation
•Ventilation is the stander practise to prevent Fire Damp explosion.
• Regular inspection is needed to the suspected area.• The accumulation of Fire Damp should not exceed the lower limit.
A place is not said to be completely ventilated if methane percentage is more than 1.25. In case of mines the percentage should not exceeds 0.75% for degree 2 & 3 mines.
•. If the percentage of methane exceeds 1.25, the electricity supply is cut down.
•. If the percentage of methane exceeds 1.25, the electricity supply is cut down.
2. Avoid source of Ignition
To prevent explosion, we have to avoid source of ignition. For this, electrical wires, motors, switch gears , transformers ans every electric appliance should be flameproof.
* If you have any query you can contact...

Comments
Post a Comment